We’re Changing the Cardiology Experience
Because You Deserve Better Care.
The practice of medicine, especially preventive cardiology, is failing patients because it focuses on general guidelines based mostly on numbers: “What’s your LDL?”, “What’s your BMI?” And that’s usually where it stops. It’s dangerous because it focuses on an equation instead of the individual. You are not your numbers. Your body is unique and deserves to be treated as such. We need a transformative shift in cardiology and preventive health care that considers you as an individual.
Let’s Talk
Send us a message and let us know how we can help you.
Introducing
Concierge Preventive Cardiology
with Dr. Scher
What if you could combine…
Now with Dr. Scher’s Concierge Preventative Cardiology, you can!
WELCOME TO
BOUNDLESS HEALTH WITH DR. SCHER
a revolutionary approach to optimizing your health and life!
Find out if this works for you
Connect with Dr. Scher today to see if this model is right for you.
Let’s Talk
Send us a message and let us know how we can help you.
Meet Dr. Scher, MD
CREATOR OF CONCIERGE PREVENTIVE CARDIOLOGY

Hi, I’m Dr. Bret Scher, and I’m changing the direction of preventive cardiology to better you with the care you deserve. I’m also the CEO and Lead Physician at Boundless Health and the Low Carb Cardiologist. I spent the past 15 years as a frustrated cardiologist. My patients weren’t achieving their optimal health, and I didn’t have the time or resources to guide them. That’s why I am revolutionizing my practice of medicine, and why I sought out additional certifications in lipidology, nutrition, personal training, functional medicine, and behavioral change.
It is through this specialized training and working with thousands of patients I recognized how to provide better care. Your health is too important to trust to guidelines designed for the ‘average’ person. You are not average, nor should you want to be!
I also recognize the need for better access and convenience. That’s the heartbeat behind Concierge Preventive Cardiology: open access so together, we can evaluate every facet of who you are and how you can best achieve your goals.
I’m glad you’re here. It tells me you know you deserve better care. I can’t wait to get started finding your path to true health.
Bret Scher, MD FACC
Board Certified Cardiologist and Lipidologist
Yes, People LOVE Dr. Scher’s Approach

We had an incredible turnout for our Webinar, aimed to help you transform your health in 2019. As a result, we decided to create a blog post that includes the full webinar recording, as well as an overview of the learnings for those that were unable to attend.
Webinar Recording
Webinar Overview
Cardiovascular Disease Is the #1 Killer for Men and Women
- 1/3 of all Americans die from Cardiovascular disease
- Around 92 million Americans are living with CVD
- Every 34 seconds someone suffers a heart attack
- Annual health expenditure and lost productivity from CVD ~$330 billion
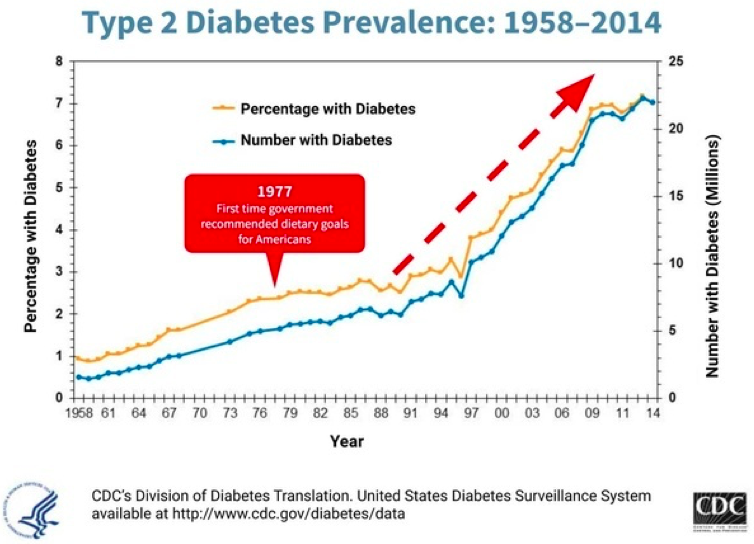
It’s been estimated that 50-80% of these are preventable! Unfortunately, our healthcare system and associated lifestyle guidelines have failed to prevent disease. We could say at best they have failed to prevent heart disease, obesity and diabetes. At worst they have been implicit in its prevalence. While this graph doesn’t show causation, it certainly shows the association of instituting national nutritional guidelines and the rise in diabetes.
Drugs Don’t Fix the Problem
- 60% of Americans take at least 1 prescription drug
- 15% take more than 5 drugs
- Despite this, our overall health and life expectancy continue to decline
HEALTH IS NOT THE ABSENCE OF DISEASE!
In this webinar, we will discuss how to be your own best advocate, why low carb, high fat nutrition should be an option for everyone, and how lifestyle really is the best medicine.
3 Interventions to Improve your Healthcare Experience and Be Your Best Advocate
- Make sure your doc is working with accurate information! Lipids and blood pressure are two prime examples of when doctors make decisions based on limited and faulty information.
- Get your questions answered by writing them down ahead of time so you don’t forget anything and tell your doctor at the beginning of the appointment that you have some questions you’d like to ask at the end.
- Make sure you understand the purpose and benefit of each and every medication. Not some vague answer like “It will improve your cholesterol,” or “It will lower your blood pressure.” Rather, “what impact will it have on my longevity and quality of life?” Will I live longer? Will I feel better? What are the chances the drug will actually benefit me? These are the questions we need answered.
Why Low Carb, High Fat Nutrition Should be an Option for Everyone!
LCHF vs Low Fat Diets
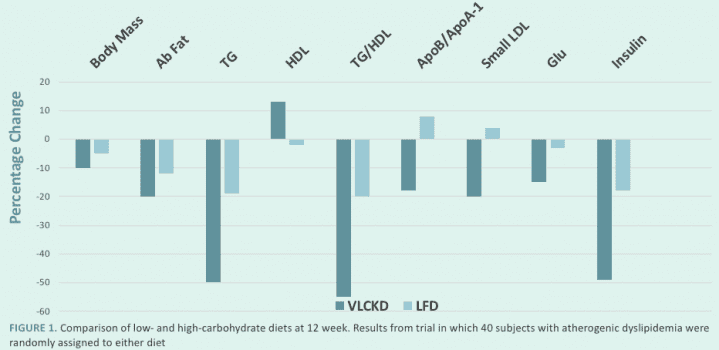
LCHF Benefits
- Decreased hunger, increased energy, mental clarity
- Treats metabolic syndrome/insulin resistance
- Better weight loss
- Improves overall cardiovascular risk for most people
LCHF may not be the best for everyone, but it certainly should be an option for everyone. If you want tips that do work for everyone, follow these bonus tips for weight loss and overall health!
- Don’t drink your calories – even “natural” drinks are full of unnecessary calories. Think about it this way, you would drink a glass of orange juice, but would you really sit down eat the 5 or so oranges it takes to make it? If not, why drink that same amount?
- Get rid of “Food Delivery Systems” – Think about the big sandwiches or burritos we see everywhere in our culture. What is the food? The stuff in the middle! The meat, the cheese, the veggies. What is the unnecessary food delivery system? The bread, the tortilla, the outer layer that has a fraction of the nutrients and a multitude of the carbs!
Lifestyle Really is the Best Medicine!
Science says lifestyle, not drugs, reverse disease:
- NEJM study reported findings on patients at highest genetic risk for heart attack, over 90% more likely to suffer heart attack. Those with healthy lifestyles had a 50% reduced risk with no drugs and no surgeries!
- JACC study found 85% of all heart attacks could be prevented with greater attention to lifestyle.
- A 2018 British Journal of Sports Medicine study found that increasing walking pace to “brisk” for those over 50 reduced all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality by 20-24%.
Why is it so hard?
We have all been told that in order to be healthy, we need to eat less, move more, and reduce fat in our diets. But if that is the case, why is it that only 12% of Americans are metabolically healthy, and only 3% of Americans follow a healthy lifestyle?
Because the simple Eat Less, Move More, Reduce Fat approach DOESN’T WORK!!!
I want to assure you that it’s not your fault, you’ve been given the wrong information.
“I was always told I simply didn’t have enough willpower to stick to a diet. I couldn’t understand why I was always hungry and craving foods. I figured it was all genetics. But working with Dr. Scher showed me there is a better lifestyle that I can stick with and still feel great and enjoy my life! Thanks Dr. Scher!”
- E
Keys to Making Lifestyle Change Stick
- Beware of one-size-fits-all nutrition and lifestyle claims
- Individually tailored and flexible nutrition is the key.
- When you eat is just as important as what you eat
- Move your body more
- Get Serious about your sleep
- Don’t be afraid to test and adjust
A Word of Caution
Don’t try to Change Everything at one time.
Choose YOUR most important first step (nutrition, stress, fitness, etc.) and work on that until a new habit is created!
And remember, you don’t have to do it alone! Working with an expert who can help you on your health journey will increase your likelihood for long term success.
As you can see, this was a quick tour to highlight the main points in the webinar. To get the full benefit, I recommend watching the full recording to get all of the context and be able to see the Q&A session at the end.
If you want to get the full experience, here is that recording again:
If you’d like to see the date and content of our next webinar, or be notified when our next webinar will be, please visit our Webinar Page.
I hope you enjoyed this recording, and that we will see you at the next live webinar!
Thanks for reading,
Bret Scher MD FACC
I live in McAllen, Texas, where it’s difficult to find a doctor who’s knowledgeable on the benefits of a low-carb lifestyle. Because I battle a high A1C AND high cholesterol, I reached out to Dr. Scher for a consultation to monitor my blood work and develop a plan that will keep my heart healthy and my A1C in check. Before our video-consultation, he responded personally to every question I had via email. When I first reached out, I figured it would take at least a month or more to schedule our consultation, but to my surprise, it was planned just over a week from my initial email!
I like Dr. Scher’s commonsense approach to a healthy lifestyle. He came up with a very-easy-to-follow plan and agreed to review my bloodwork every 6-8 weeks to make sure I’m on the right track. Because of my family’s history, it’s comforting to know I have a cardiologist monitoring my health so that I can prevent a significant problem down the road.
Nicole Southwell
Dr. Scher’s six-month program has been helping me make progress on my health journey. I started the program five months ago after I decided to get more serious about my health and reduce my coronary heart disease (CHD) risk by making healthy diet and lifestyle changes.
The program is not only providing me with excellent video and written content that helps me progressively realize my health goals with effective plans of action, but also individualized attention via email and with monthly video calls with Dr. Scher. I’m grateful for this individualized attention and for Dr. Scher’s insights and suggestions. His advice has honored my preference to continue following a low-carbohydrate lifestyle and has helped me select appropriate macronutrient targets such as daily intake of carbohydrates and protein based on my goals and his review of my medical history and lab test results.
Ken Carrillo
Chemical Engineer

Are you interested in trying a Low Carb-High Fat/Ketogenic lifestyle? If so, great.
Are you looking to your doctor for support in this diet? If so, tread gently.
The medical community has engrained false beliefs that LCHF lifestyle is dangerous to your health. We can blame it on Ancel Keys. We can blame it on an over emphasis on LDL-C. We can blame it on Big Pharma. We can even blame it on the rain! Whatever the reason, you may not get a warm and receptive response from your physician.
But there is hope. Here are my top 6 Tips on How to Talk to Your Doctor About The LCHF/Keto Lifestyle.
1. First, ask for your doctor’s opinion about LCHF
Doctors are people too. How would your spouse react if you said, “I’m no longer taking out the trash/doing the dishes/making dinner. It doesn’t work with my personal philosophy of house chores and we are going to change this. Now.” I hope you have a comfortable couch, cause that’s where you will be sleeping.
Picture instead, “Hi Honey. I was thinking that we may want to reassign some of our house chores to help things get done better and more efficiently without putting too much strain on either of us. What do you think about that? Do you have any thoughts how you would like to change things?” That sounds better, right?
The same approach applies to your doctor. Just don’t start by calling your doctor honey. That’s just awkward. Don’t say, “Hey Doc, I’m going LCHF and need you to order x, y and z blood tests on me now and again in 6 months, and help me get off my meds.” Instead, try a kinder, gentler approach. “Hi Doc. I was thinking of ways to be more proactive about my health. What I have done thus far has not worked as well as I have liked. I have heard a lot about LCHF as a way to lose weight, reduce insulin levels, improve blood glucose control, and feel better. I was thinking of trying it. What do you think about that?” You may not immediately get the answer you want (for instance, I am still taking out the trash every week), but you have opened the lines of communication in a much less confrontational way, which can set you up for success as we discuss other tips below.
2. Measure the effects of Keto on your body with a medical trial
If your doctor is hesitant about you trying LCHF/Keto, suggest a 3- or 6- month trial. Establish what you want to monitor (here’s an eBook I created to help you get started: 10+Medical Tests to Follow on the LCHF Diet). Check what you would like to monitor at baseline and then at the 3-6-month mark. Emphasize you want to experiment to see how your body responds, and that you want his/her expertise in helping analyze the labs to help you progress safely.
Also, if you are on medications for blood pressure, blood sugar or lipids, you will want their guidance with these. Emphasize how you want him or her on your team to help you on your journey and temporary experiment. It is hard to resist when someone genuinely wants your help and thinks you can play a role in their improvement!
3. Show them your results!
Don’t gloat, don’t brag, but make sure you follow up with your doctor and tell them everything you feel and have measured. Do you have more energy? Less stiffness or inflammation? Are your pants fitting looser? And of course, follow up on all the labs to look at the whole picture. You will be surprised how often your doctor will then turn to you and ask you what you have been doing. If they have the time, they will likely say “Tell me more about that.” Yes! This is your opportunity to teach them the power of LCHF/Keto. Then, when the next patient comes around, they won’t be as resistant, and may even start to suggest it themselves. The patient becomes the teacher!
4. Find a doctor who will listen
Our healthcare system is messy. No question. We don’t always have freedom to choose our own doctors. But that doesn’t mean it is impossible to change. Here is a hint: If your doctor isn’t open minded enough to try a self-directed experiment with you, what else are they close minded about? Maybe it is time for a change anyway.
It may not be easy to find a doctor with an open mind who takes your insurance, is geographically desirable, and who is accepting patients, but there are some tricks you can use. Look for a doctor who has been in practice more than seven years, but less than 20 years. In my experience, this is the critical “open minded” window. They have been in practice long enough to be confident in their own skills and are willing to stray from “what everyone else does.” On the other hand, they have not been in practice so long that “That’s the way I have always done it” becomes the reason for their care.
Look for doctors with interests in prevention, sports medicine, or integrative medicine. These suggest more interest in health and less interest in the standard “pill for every ill” medical practice. Lastly, people are developing lists of Keto-friendly doctors online. While these may be small at present, they are growing quickly and hopefully can help you find the right doctor for you.
5. Seek online Keto support
Numerous online sites exist to help you with you transition to a LCHF lifestyle. I have built my blog and Low Carb Cardiologist Podcast to provide information and support on those who are embarking on their healthy lifestyle journeys, with a lot of information about Keto and LCHF.
Some other sites I recommend are DietDoctor.com, 2KetoDudes podcast, and Ketovangelist podcast, to name a few.
6. Take control of your own healthcare journey
As nice as it is to have your physician on board with your health decisions, it is not always needed. As Brian Williamson from Ketovangelist said to me on his podcast, “If your doctor is more interested in your health than you are, then you are in trouble!” I agree with that sentiment, and I encourage everyone to be the driver in their own healthcare. You can still choose to try the LCHF lifestyle even without your doctor. Look for a reputable second opinion doc who is willing to help open lines of communication between you and your doc. That is one of the services I enjoy providing the most. Since I speak the same language, I can usually help someone start the conversation with their doctor.
In addition, online sites such as WellnessFx.com allow you to get your blood drawn and seek consultations with health care providers (Disclaimer: I am one of those providers and get paid for my services. Another disclaimer: I love doing it). If you go this route, I encourage you to then bring your results back to your doctor (See number 3 above). You can now become the teacher, young Jedi.
There you go. With these six simple tips and resources, you will be well on your way to safely adopting a Keto lifestyle. Doctors are people too. Just like everyone else, we like to be needed, we like to be helpful, and we don’t like being told what to do. I just need to remember that the next time my wife “needs” me to clean the toilet….
Thanks for reading.
Bret Scher, MD FACC
Founder, Boundless Health
What Does My Cholesterol Level Mean?
Depending on how you look at it, cholesterol can be an incredibly simple topic, or an incredibly confusing one. Contemporary medicine teaches that cholesterol is “bad” and should be low. That seems pretty simple, right? Get it tested, if it’s high, start a drug to lower it.
Times have changed. Now, cholesterol is much more complex, and we all need to be armed with knowledge before we sit down with our doctors to evaluate our cholesterol levels.
Here is my guide to you and your doctor for evaluating your cholesterol.
1. Understand the difference between Total Cholesterol (TC) and high density lipoprotein (HDL) and low density lipoprotein (LDL)
If you doctor is referring to your total cholesterol (TC) and is making decision based on your TC— Run, don’t walk. Run away and find another doctor. TC is comprised of low density lipoprotein (LDL), so-called “bad cholesterol” even though it isn’t bad. High density lipoprotein (HDL), so-called “good cholesterol”, and remnant cholesterol (VLDL and IDL). Initial studies in the 1960s and 70s looked at TC and risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and found a weak association. That was prior to when scientists learned how to measure LDL and HDL.
Studies then looked at the individual lipoproteins (i.e. LDL and HDL) and found the higher the LDL, in general, the higher the risk for CVD. And the higher the HDL< the lower the risk of CVD. So, while talking about TC was cutting edge in the 60s and 70s, it is woefully outdated today. That is why if your doctor is still evaluating and treating TC—Run!
2. Does Your Doctor Know Your TC to HDL and TG to HDL Ratios?
If your doctor does not know your ratios, this is another reason to run away and find another doctor (We are doing lots of running here, bonus exercise!) Studies in the early 2000s and more recently have shown that total cholesterol to HDL ratio (TC:HDL) and triglyceride to HDL ratio (TG:HDL) are BETTER predictors of cardiovascular risk than isolated LDL, TC or HDL.
By incorporating TG and HDL into the analysis, these ratios incorporate the impact of remnant cholesterol and track with insulin resistance, both strong predictors of CVD. These ratios are calculated from a standard lipid profile, so they do not require any special testing or special labs. They are widely available for everyone to see. So if your doctor is not using them to evaluate your lipids, it’s time to find a new one.
3. Understanding a Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) diagnosis
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a diagnosis that requires (wait for it…) a family history! As the name suggests, it is an inherited condition passed from generation to generation. All too often, doctors will see an LDL level over 190 and make the diagnosis of FH. If your doctor makes that diagnosis that based on level alone without a family history, run!
There is a well-accepted scoring system, The Simon Broome Criteria, to help determine if someone has FH. This equation factors in age of diagnosis, absolute level of LDL, in addition to family history of early onset hyperlipidemia or early onset heart disease. It makes a big difference if you have FH or not. Don’t let your doctor label you as having FH without applying the full criteria. Just wait for the look on their face when you respond, “What was my Broome score? Did it confirm I have FH?” and hope you don’t hear crickets.
4. What is Advance Lipid Testing?
Advance lipid testing may be helpful. And it may not. Advanced lipid testing can tell us the size, density, and inflammatory characteristics of our lipoproteins. This can help further risk stratify the potential danger of our lipids. For instance, small, dense LDL tend to correlate more strongly with CVD, whereas so-called pattern A LDL (the larger, less dense version) does not correlate as well.
Here is the interesting part. Those with high TG and low HDL almost uniformly have small dense LDL and increased inflammation. Conversely, those with low TGs and high HDL have Pattern A, larger less dense LDL. Are you starting to see a pattern? Low TG and high HDL=good. High TG and low HDL=bad.
Sometimes, however, there can be variation in this equation. Therefore, I usually suggest people get advanced lipid testing one time to see if their results correlate. If they do, then you can just follow your ratios to predict your advanced results. Why not get them all the time? They are frequently not covered by insurance and can be expensive.
5. Interpret your lipids in context
Lipids don’t exist in a vacuum. They exist in your body, so it’s important to take into account what else is going on in your body. Insulin resistance and inflammation can directly affect your lipids and increase your risk in general. Hypertension, obesity, and family history of heart disease also play crucial roles in determining your risk.
Therefore, if your doctor checks only your lipids and bases decision on those labs alone—Run! Instead, you should get a hsCRP, Hgb A1c, fasting glucose, insulin and HOMA-IR, BP measurement, family history assessment, and complete history. This is the context in which your lipids should be evaluated. Not alone in a vacuum.
6. Why test a risk factor that may be related to CVD risk when you can test the disease itself?
Good question, right? To truly know what your lipids mean to you, you also need to know if you have evidence of CVD. Coronary artery calcium scores and Carotid Intima Media Thickness (CIMT) are two easy, relatively inexpensive tests, that you can get to show you whether or not you have current evidence of CVD. The presence or absence of disease significantly impacts the risk of lipid levels.
So, What Does Your Cholesterol mean to You? It depends.
It depends on many factors, and only by evaluating ALL of those factors can you truly know what impact your lipids may be having on our health. Anything short of this evaluation is an inadequate and antiquated approach to lipids.
Now you are forewarned and forearmed, and you can walk into your doctor’s office ready to ask the important questions and help guide the workup so that you can know what your cholesterol means to you.
Thanks for reading, and as always, please let us know If you have any comments or questions.
Bret Scher MD FACC
Founder, Boundless Health
www.LowCarbCardiologist.com
TAKING YOUR NEXT STEP
WITH BOUNDLESS HEALTH AND DR. SCHER
We are excited to help you in your quest for better health! If you are ready to take the next step, your annual membership will give you access to:
START A CONVERSATION
Connect with Dr. Scher to see if this model is right for you today.
Let’s Talk
Send us a message and let us know how we can help you.
